torsion in testes|how to know if you have testicular torsion : exporting Testicular torsion is a serious and painful condition that affects your testicle (s). If you experience testicular torsion, the spermatic cord twists and cuts off blood flow to your testicle. If you don’t . Resultados de lotería de Animalitos: Revisa los resultados d.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Tire as suas dúvidas aqui! Explore a nossa biblioteca e tenh.

why do my testicles hurt
Testicular torsion is a serious and painful condition that affects your testicle (s). If you experience testicular torsion, the spermatic cord twists and cuts off blood flow to your testicle. If you don’t . Testicular torsion is when a your testicle twists around. (The word torsion means “to twist.”) The motion also twists the spermatic cord that connects to the testicle. . Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .
Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, . Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a.Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and . Emergency Symptoms. Other emergency signs of testicular torsion include: Blood in your semen (whitish fluid your penis ejaculates) Change in your scrotum’s skin color, including redness or bruising. Introduction. Testicular torsion refers to the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in . Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage .
Causes of testicle pain. Sudden, severe testicle pain can be caused by twisting of the testicle (testicular torsion). This is a serious problem that can lead to the loss of the testicle if it's not treated quickly. Less serious causes of testicle pain include: an infection (epididymitis) an injury; an inguinal hernia; a build-up of fluid (cyst)Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. A thorough history, the presence of a painful and swollen testis and testicular ultrasonography . Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours. Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and .
The recommendations on management of testicular torsion are based on the European Association of Urology (EAU) guideline Paediatric urology [Radmayr, 2021], the Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) joint publications Asymptomatic scrotal swelling, commissioning guide [] and Management of paediatric torsion, commissioning guide [], and expert opinion in review . Testicular torsion is the rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord, which can obstruct its blood supply and lead to necrosis. Most often, testicular torsion affects young adolescents. The most common cause is the congenital failure of the testicles to strongly attach to the scrotum. Symptoms can include sudden severe pain of the .
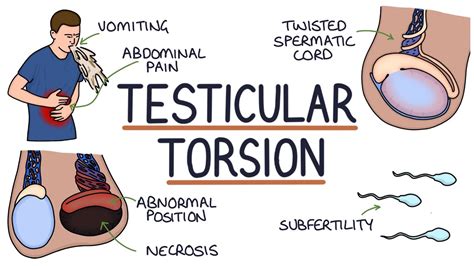
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle twists around the cord (the structure extending from the groin to the testes that contains the sperm ducts and blood vessels), like an apple twisting on its stem. When the blood vessels are twisted, they can cut off circulation to the testicle and cause permanent damage, including death of the .
Testicular torsion is an emergency: When it happens, a guy needs surgery — fast. Saving the testicle becomes more difficult the longer the spermatic cord stays twisted. As a general rule: within about 4–6 hours of the start of the torsion, the testicle can be saved 90% of the time;
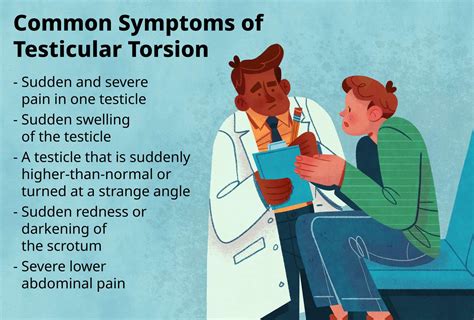
Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle twists inside of the scrotum so much that it chokes the blood flow to the testicle. "This leads to sudden, severe pain in the belly and testicle, but guys may try to tough it out or not clearly communicate the symptoms," says Dr. Schlomer.
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility.Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting.What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion happens when one of your testicles twists around. Each testicle is attached to a spermatic cord, which contains blood vessels that carry blood to the testicle. In testicular torsion, this becomes twisted (called torsion) and blocks the flow of blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is an emergency. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency — it occurs when blood flow to the testicle stops, causing sudden and often severe pain and swelling.
Torsion of the testicular appendages is considered the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal children and may even be the single most prevalent cause of pediatric orchalgia.[1] Therefore, it should be included in the differential diagnosis for any male presenting with an acute scrotum, particularly in the pediatric age group.[1] Two testicular .
testicular torsion symptoms and signs
What is testicular torsion?The testicle has attachments that hold it in place in the scrotum. Occasionally, these attachments do not exist and the testicle can twist. When the testicle twists on itself it causes the blood supply to kink and .Testicular torsion is a medical emergency. It happens when the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, rotates and becomes twisted. This cuts off the testicle's blood supply and causes sudden pain and swelling. .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of . Torsion of the testes is a surgical emergency, since it causes strangulation of gonadal blood supply with subsequent testicular necrosis and atrophy. Acute scrotal swelling in children indicates torsion of the testes until proven otherwise. The cremasteric reflex is most commonly performed in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain and the assessment for testicular torsion that is commonly associated with an apparent loss of the reflex.[1][2][3] Superficial reflexes are motor responses that occur when the skin is stroked. The cremasteric reflex is a superficial reflex found in human . Testicular torsion is twisting of the spermatic cord, which supports the testes in the scrotum. When this occurs, blood supply is cut off to the testicles and nearby tissue in the scrotum. This may cause permanent damage to the testicle. Causes.
Torsion of the appendix testis is a twisting of a vestigial appendage that is located along the testicle. This appendage has no function, yet more than half of all boys are born with one. Although this condition poses no threat to health, it can be painful. Usually no treatment other than to manage pain is needed. Testicular torsion is a urological emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischaemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies. Testicular torsion means that your testicle has rotated in the scrotum. This can wind up the spermatic cord, cutting off blood supply, nerve function, and sperm transport to your scrotum.
Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency when a testicle twists around the spermatic cord, cutting off the blood supply. While it can occur without pain, most people experience severe pain in the .Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.
Heat Sealer Tester service
webSultanbet adalah situs taruhan dan kasino terbaik yang menawarkan berbagai pilihan permainan, bonus, dan layanan. Anda bisa menikmati sportsbook, kasino, kasino langsung, permainan virtual, dan banyak lagi. Daftar sekarang .
torsion in testes|how to know if you have testicular torsion